No products in the cart.

✨ A Comprehensive Exploration of Shamanism ✨
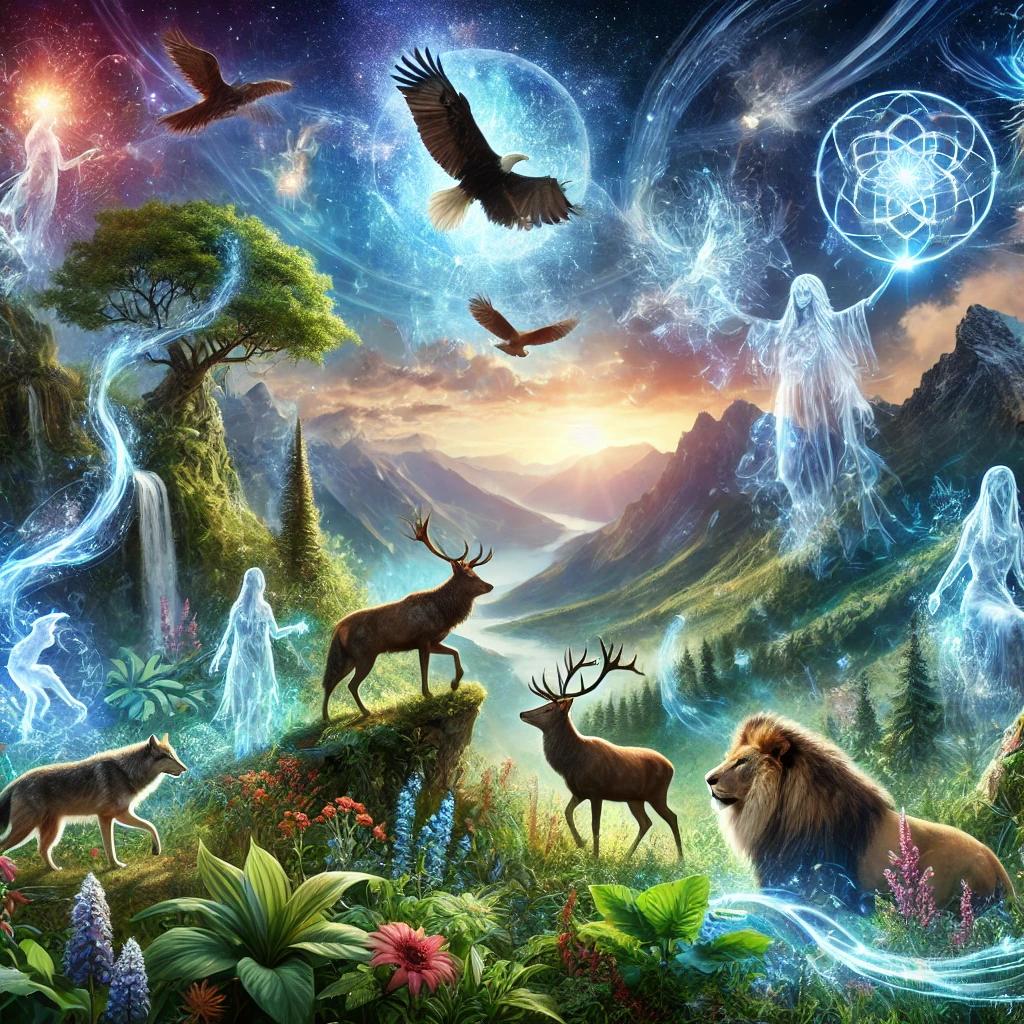
Shamanism is one of the oldest spiritual practices in human history, dating back tens of thousands of years. It is a system of beliefs and practices involving communication with the spirit world and interaction with supernatural forces. Shamanism exists in various forms around the globe, reflecting the diverse cultures and traditions that have integrated these ancient ways into their lives. This article delves into the origins, practices, and philosophies of shamanism, exploring its manifestations in different parts of the world.
🎨 Origin of Shamanism
Shamanism likely emerged in prehistoric times, as early humans sought ways to understand and interact with the natural world around them. The word “shaman” is thought to have originated from the Tungusic-speaking peoples of Siberia, derived from the word šamán, meaning “one who knows.”
- Role: These early practitioners were believed to possess unique knowledge and abilities, enabling them to communicate with spirits, heal the sick, and guide their communities through spiritual crises.
- Evidence: Archaeological findings suggest that shamanic practices may date back at least 30,000 years, with depictions of shamans seen in ancient cave art. These early images often show figures dressed in animal skins or masks, surrounded by symbols of transformation and power.
🌠 Core Elements and Philosophy of Shamanism
Though shamanism varies greatly across cultures, it generally shares some key characteristics:
- Connection to the Spirit World: Shamans serve as intermediaries between the human world and the spiritual realm. They enter altered states of consciousness, such as trance, to communicate with spirits, ancestors, or deities.
- Healing: Shamans act as healers, addressing illnesses believed to stem from spiritual imbalances, curses, or malevolent spirits. Healing methods include rituals, herbal medicine, energy work, and exorcism.
- Rituals and Ceremonies: Shamanic rituals often feature rhythmic drumming, chanting, dancing, or singing to induce trance states. These ceremonies are performed for healing, protection, hunting success, or to mark significant life events like birth, death, or marriage.
- Animism: Many forms of shamanism embrace animism, the belief that all living things and natural objects have spirits or souls. Shamans communicate with the spirits of animals, plants, rocks, and rivers, seeking guidance and assistance.
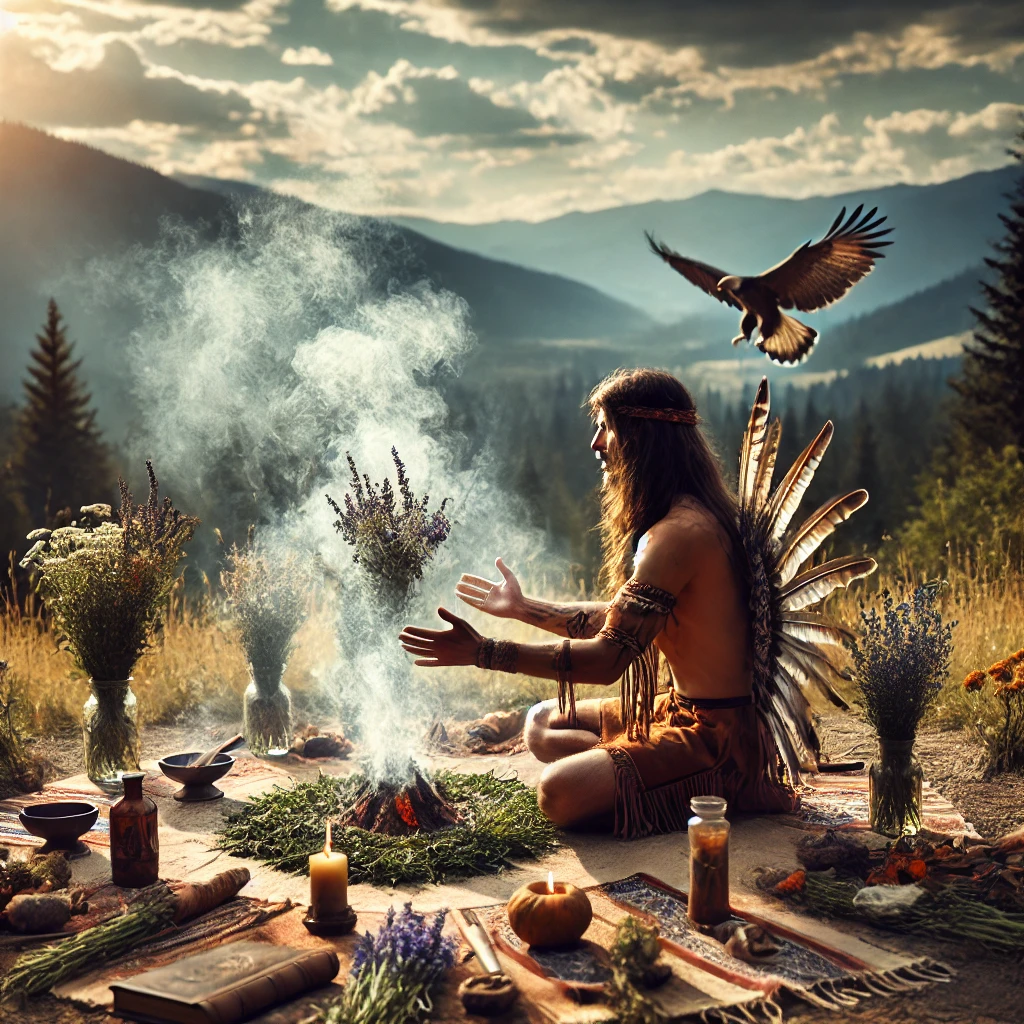
- Altered States of Consciousness: Shamans achieve altered states through drumming, fasting, meditation, or the use of psychoactive plants like ayahuasca or peyote. These states enable journeys to other realms for guidance, healing, or prophecy.
🌱 Shamanic Practices Around the World
Shamanism manifests in diverse forms globally, from the icy tundras of Siberia to the rainforests of the Amazon. Here are some notable traditions:
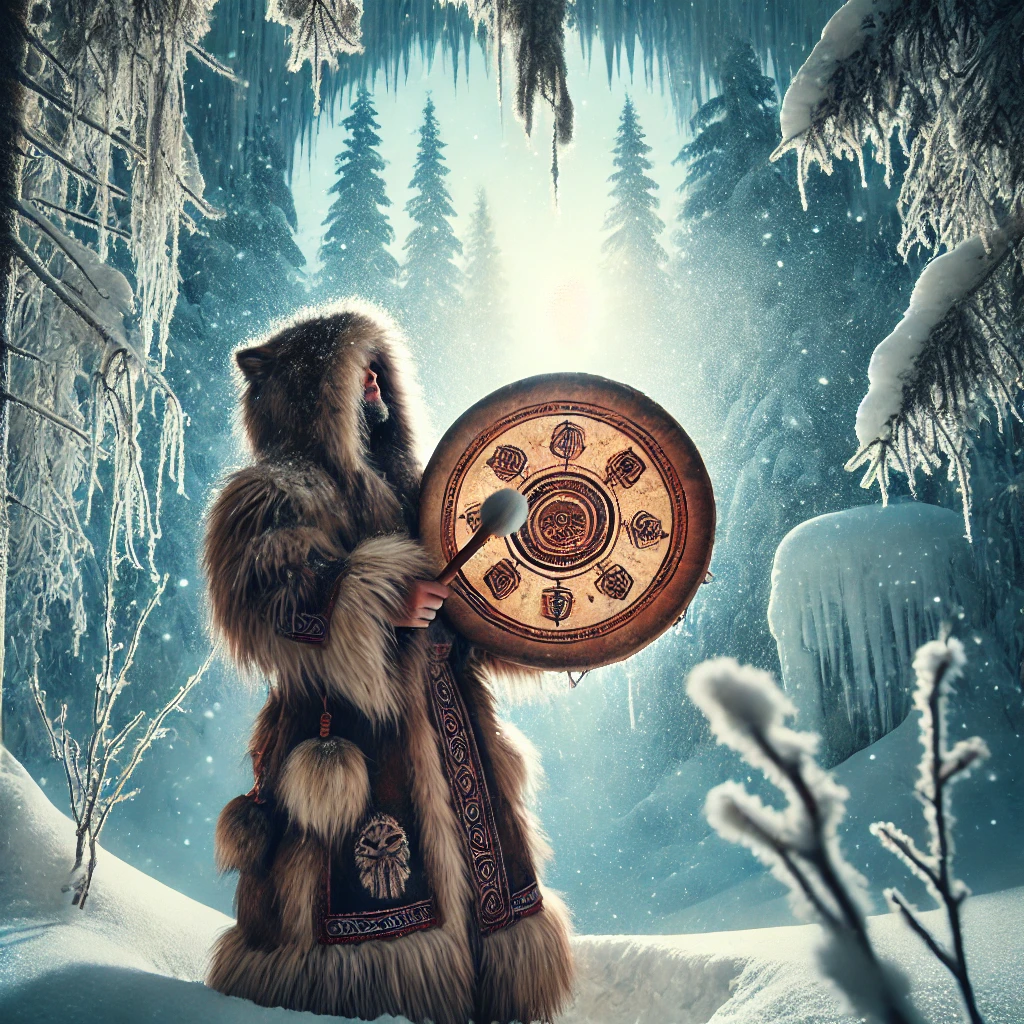
Siberian Shamanism
- Role: Siberia is considered the birthplace of shamanism. Indigenous peoples like the Evenki, Buryat, and Yakut use drumming, chanting, and dancing to enter trance states.
- Beliefs: They view the universe as multi-layered, with upper, middle, and lower worlds. Shamans travel between these realms to communicate with spirits.
- Symbols: Animal spirits play a significant role, and shamans wear costumes adorned with feathers, furs, or bones to symbolize their connection to the spirit world.

Amazonian Shamanism
- Practices: The indigenous tribes of the Amazon Basin, like the Shipibo-Conibo, use ayahuasca in spiritual ceremonies. Ayahuasca is a potent brew inducing visions and profound spiritual experiences.
- Healing: Shamans use plant spirits for both spiritual and medicinal purposes. Healing rituals involve singing icaros and using plant medicines to cleanse the body and spirit.
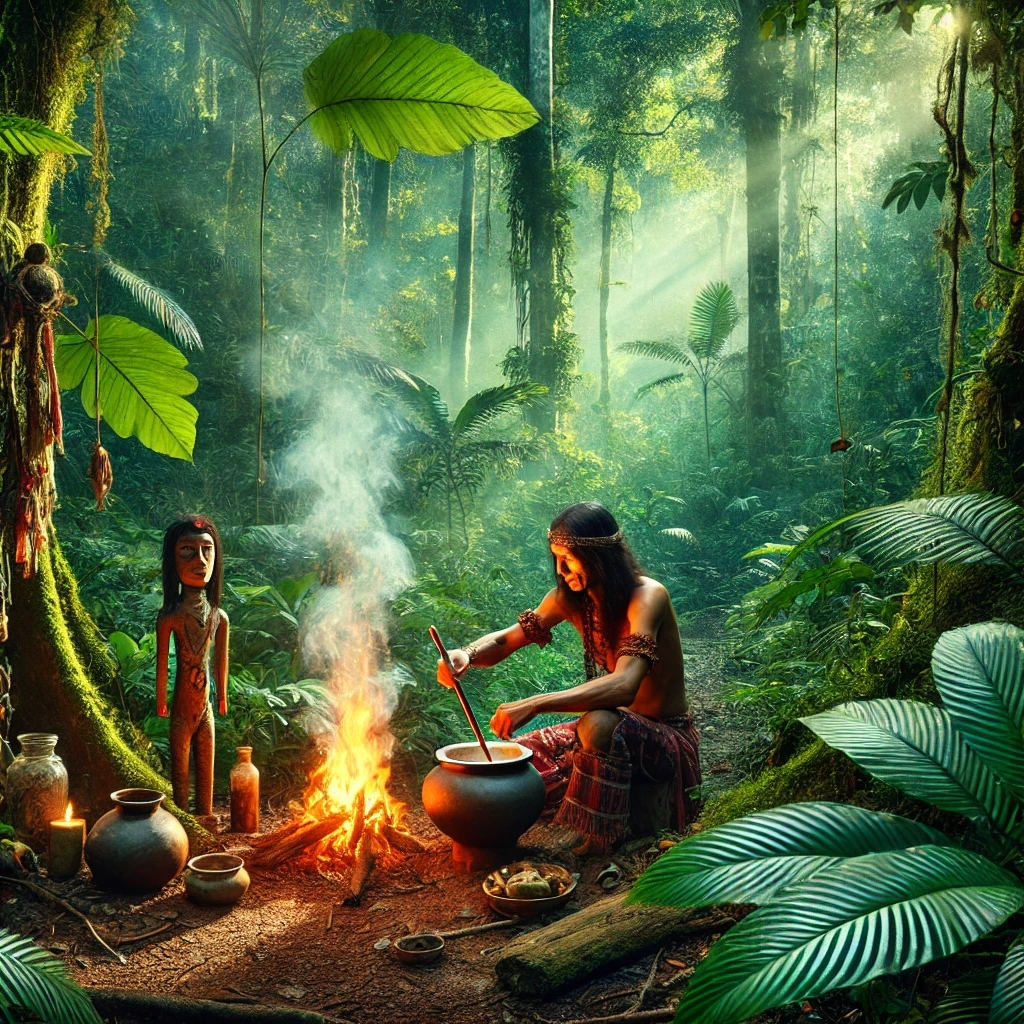

Native American Shamanism
- Beliefs: Many Native American tribes believe in the interconnectedness of all life. Their shamans, often called medicine men or women, conduct sweat lodges, vision quests, and use sacred plants like peyote or sage.
- Ceremonies: Examples include the Sun Dance of the Lakota and chantways of the Navajo, aimed at restoring harmony and balance.

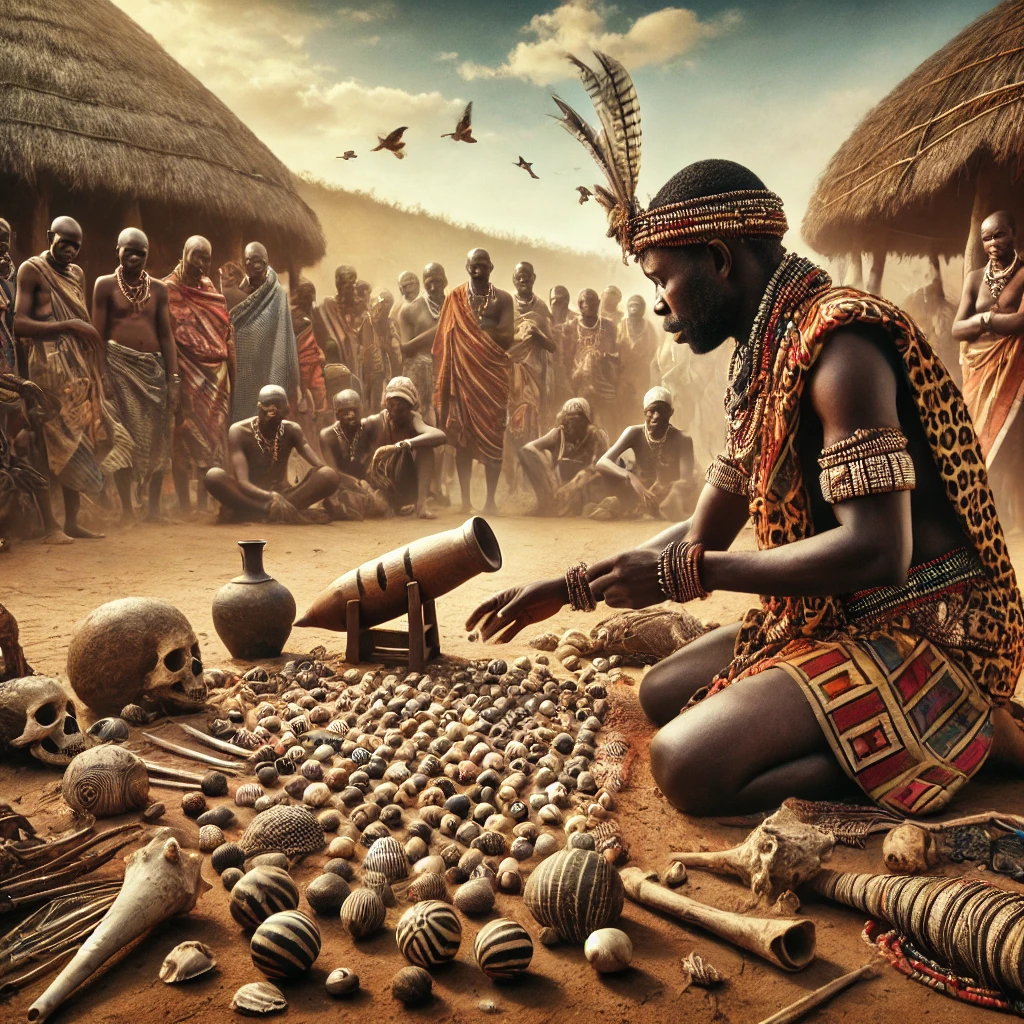
African Shamanism
- Practices: African shamans, called traditional healers or diviners, communicate with ancestors through rituals and trance states.
- Healing: They use herbal medicine, spiritual cleansing, and divination techniques, such as throwing bones, to interpret spiritual guidance.

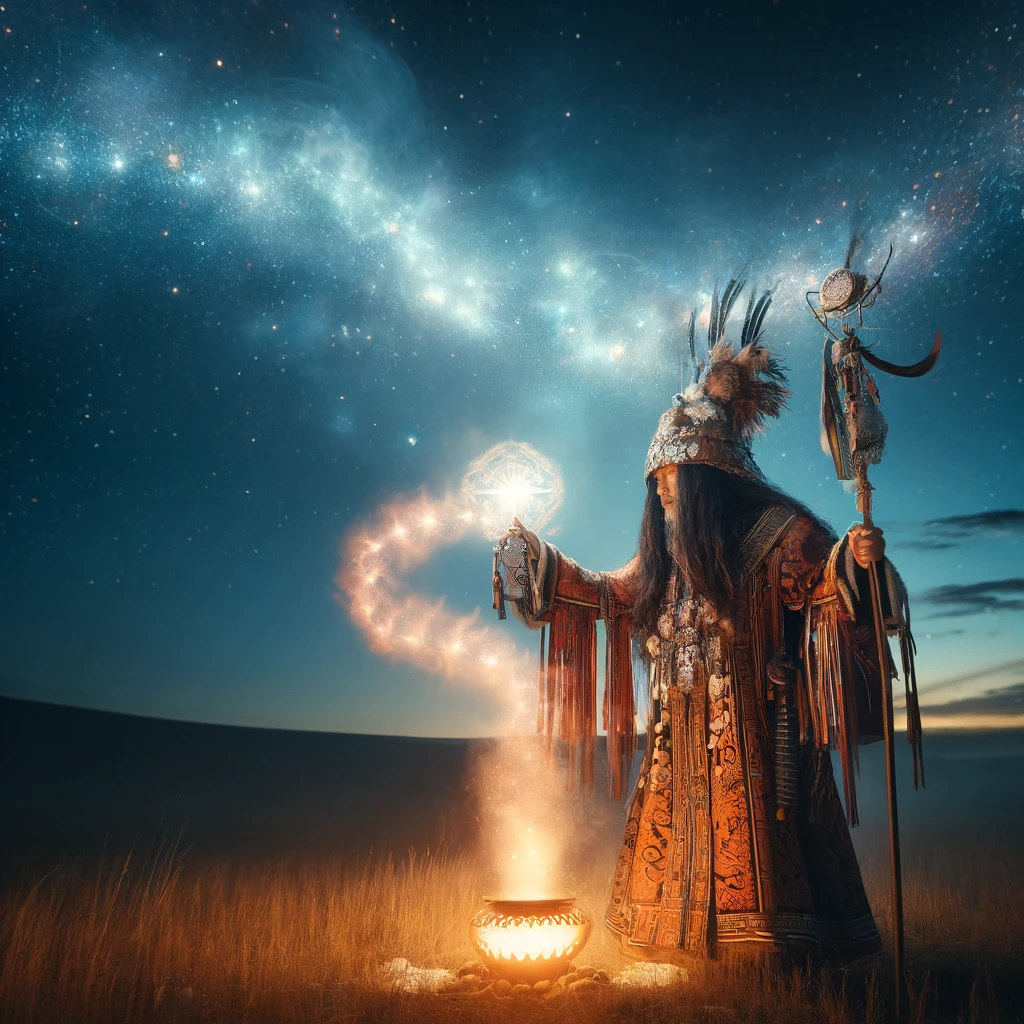
Mongolian Shamanism
- Role: Mongolian shamans (böö) act as protectors of the land, communicating with spirits of mountains, rivers, and ancestors.
- Methods: They use drumming, chanting, and elaborate costumes to connect with the spiritual world.

🌌 Shamanism in the Modern World
In recent years, shamanism has experienced a resurgence in the West, with people seeking healing and connection with nature. Modern practitioners, sometimes called neo-shamans, adapt traditional techniques like drumming, chanting, and journeying to contemporary contexts.
Global interest in Ayahuasca retreats and vision quests has popularized shamanism, though concerns exist about the commercialization and appropriation of indigenous practices.
🌟 Philosophy of Shamanism
At its core, shamanism emphasizes the deep interconnection between the physical and spiritual worlds. Shamans maintain harmony between these realms, ensuring well-being for individuals and communities.
- Respect for Nature: Animals, plants, rivers, and stars are seen as alive and imbued with spiritual power. Shamans act as guardians of this sacred balance.
- Healing and Guidance: Spiritual acts like healing and protection require alignment with the forces of nature, ancestors, and the cosmos.
🔄 Exploring Shamanic Tools and Practices
Feeling inspired? Engage more deeply by exploring our curated selection of shamanic tools and accessories. From traditional Rapé blends to ritual instruments, each item reflects the spiritual heritage and cultural richness of shamanic practices. Discover the full collection to enhance your personal journey.